Lupus –
- What is it?
- Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease that occurs when your body’s immune system attacks your own tissues and organs. Inflammation caused by lupus can affect many different body systems including but not limited to your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain, heart and lungs. Most of diagnosis are found in young women, between the ages of 15 and 44 as well as minorities i.e. African Americans, Hispanics and Asians. While research and scientist are still trying to determine what may cause this disease at this time there are no known causes attributed to someone becoming affected with Lupus. There are no known cures for lupus, however there are a few treatment options for patient affected with this disease to help manage symptom of Lupus. The research community is working daily through the help of clinical trials to finding a cure and/or more effective treatment options for patients living daily with Lupus.
- Symptoms
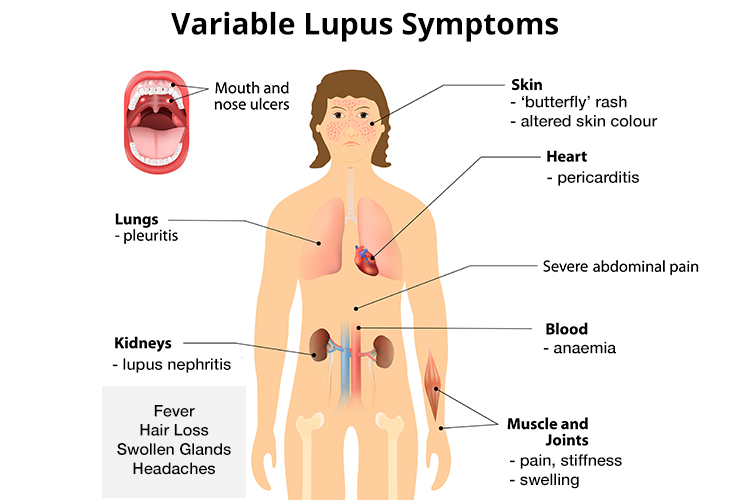
- While every Lupus case is different from patient to patient there are some common symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Joint pain, stiffness and swelling
- Butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body
- Skin lesions that appear or worsen with sun exposure (photosensitivity)
- Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to cold or during stressful periods (Raynaud’s phenomenon)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dry eyes
- Headaches, confusion and memory loss
- How is it diagnosed?
- Lupus mimics and have so many similar characteristics of so many other diseases it has taken years for physicians to truly understand and diagnose many with this disease. There isn’t no one test that can diagnose a patient with lupus however with the combination of lab test, biopsies, x-rays, symptoms and a physical exam typically help many physicians make a diagnosis of Lupus.
- How is it treated?
- Treatment for lupus may vary from patient to patient and is based on the severity of signs and symptoms being experienced. Some treatment that may be prescribed NSAIDS (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others); Steroids such as prednisone, or high doses of steroids such as methylprednisolone (A-Methapred, Medrol) for more severe cases; Antimalarial drugs such as hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil); Immunosuppressants such as azathioprine (Imuran, Azasan), mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept) and methotrexate (Trexall); Biologics such as belimumab (Benlysta); and clinical trials.
- While every Lupus case is different from patient to patient there are some common symptoms: